What is Payment Authorization?
Payment authorization (also called credit card authorization) is the step in the payment process where the issuing bank verifies the payment method. The bank confirms that the account has enough funds or available credit and ensures that the transaction does not break security or fraud rules. As a result, merchants know whether they can safely proceed.
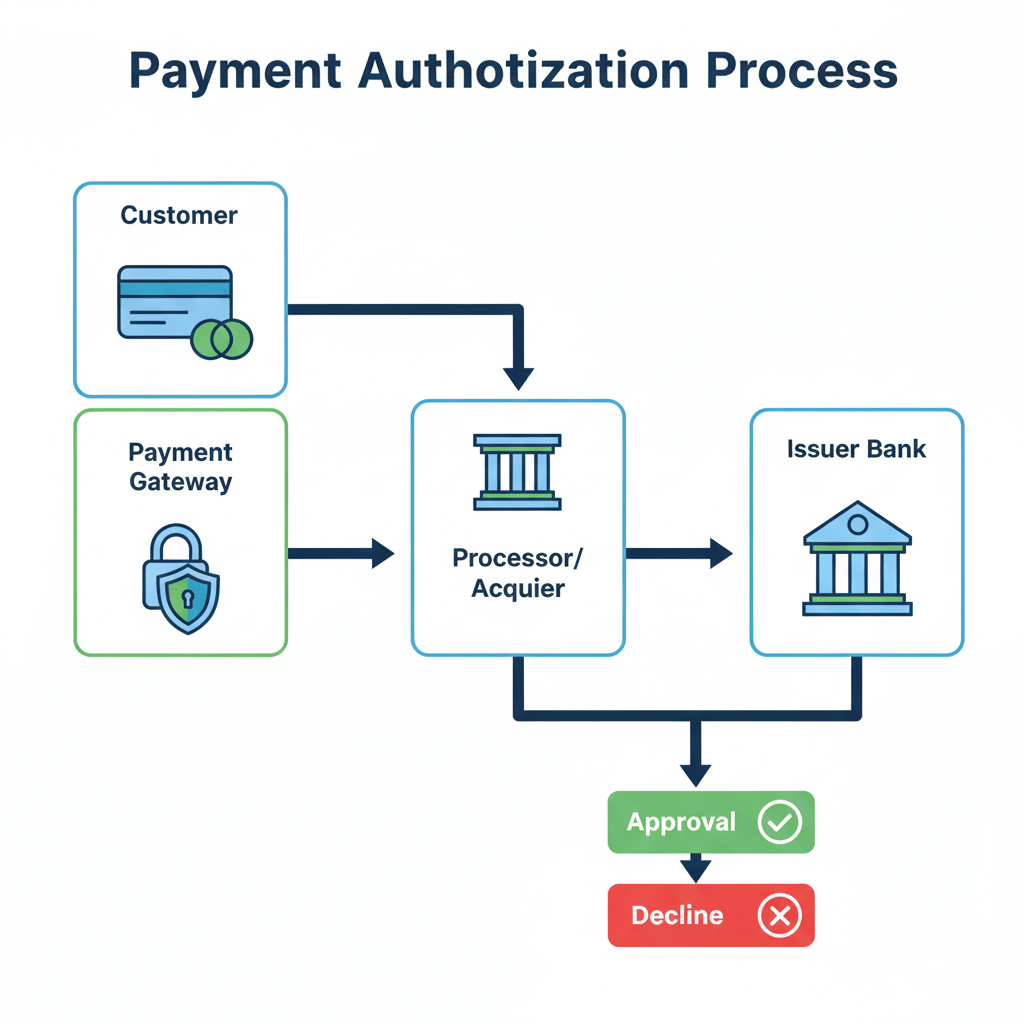
How It Works (Process Steps)
- The customer enters or provides payment details in person, online, or through a virtual terminal.
- The payment gateway encrypts the data and sends the request to the payment processor or acquirer.
- The acquirer routes the request through card networks until it reaches the issuing bank.
- The issuing bank checks card status, available funds, and fraud indicators. If the details are correct, the bank approves the request.
- The merchant receives either approval or a decline. Therefore, the business knows instantly whether to continue or stop the transaction.
Authorization vs Capture vs Settlement
- Authorization: The bank approves the payment request but does not yet transfer funds.
- Capture: The merchant submits the approved authorization and captures the funds.
- Settlement: The processor finalizes the transaction, and the funds move from the customer’s account to the merchant’s bank.
Why Payment Authorization is Important
- It prevents businesses from accepting payments without sufficient funds or expired cards.
- It reduces fraud and chargebacks because the system verifies each transaction before processing.
- It builds trust between merchants and customers. As a result, both sides enjoy safer transactions.
Common Challenges / Issues
- Some payments fail because of incorrect data, strict fraud filters, or specific bank policies.
- Authorization holds can frustrate customers when they last too long.
- Merchants must follow compliance rules such as PCI-DSS, which creates extra work. However, compliance is essential for security.
Best Practices for Merchants
- Use accurate data entry such as billing address, CVV, and card expiry to reduce declines.
- Monitor decline codes and learn from them. In addition, share updates with your payment team to improve acceptance rates.
- Adopt fraud detection tools that balance strict security with a smooth customer experience.
- Manage authorization holds carefully. For example, capture funds before the authorization expires and notify customers when holds end.